EMA 2024 GCP Report: Key Findings, Compliance Risks & How Organisations Can Strengthen Inspection Readiness
Strengthening EMA GCP Globally
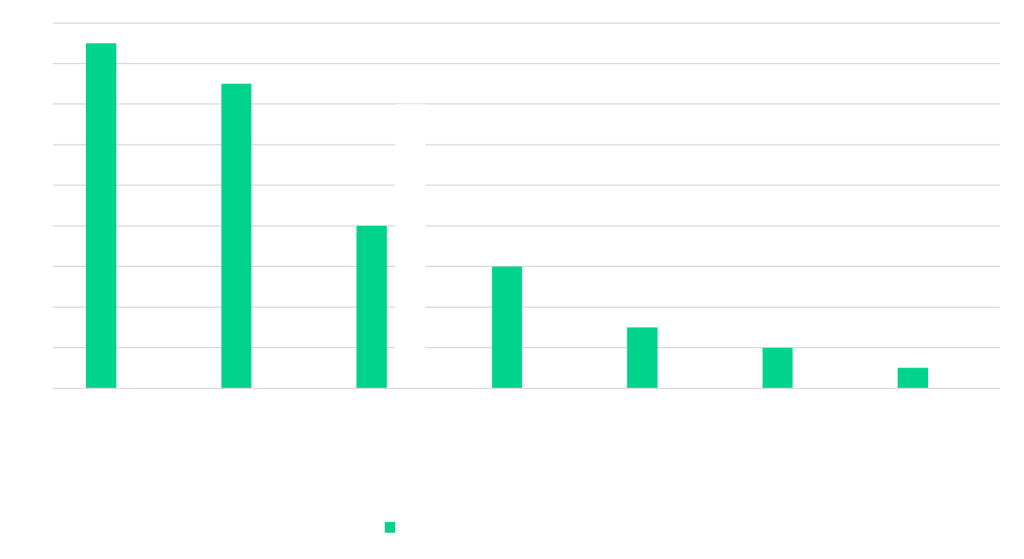
On 15th December 2025 the European Medicines Agency (EMA) published their 2024 Annual Report of the Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Inspectors Working Group. In the report they highlighted ongoing compliance challenges observed during 67 GCP inspections conducted globally in 2024, including 52 routine inspections and 15 non-routine inspections.
 These inspections were not limited to Europe. While 22% of inspections took place in the EU/EEA, a significant proportion were conducted in Asia (33%) and North America (25%), reflecting the increasingly global nature of clinical trial oversight and the EMA’s reliance on international inspection activity.
These inspections were not limited to Europe. While 22% of inspections took place in the EU/EEA, a significant proportion were conducted in Asia (33%) and North America (25%), reflecting the increasingly global nature of clinical trial oversight and the EMA’s reliance on international inspection activity.
Figure 1: Number of inspections by inspection type conducted per region
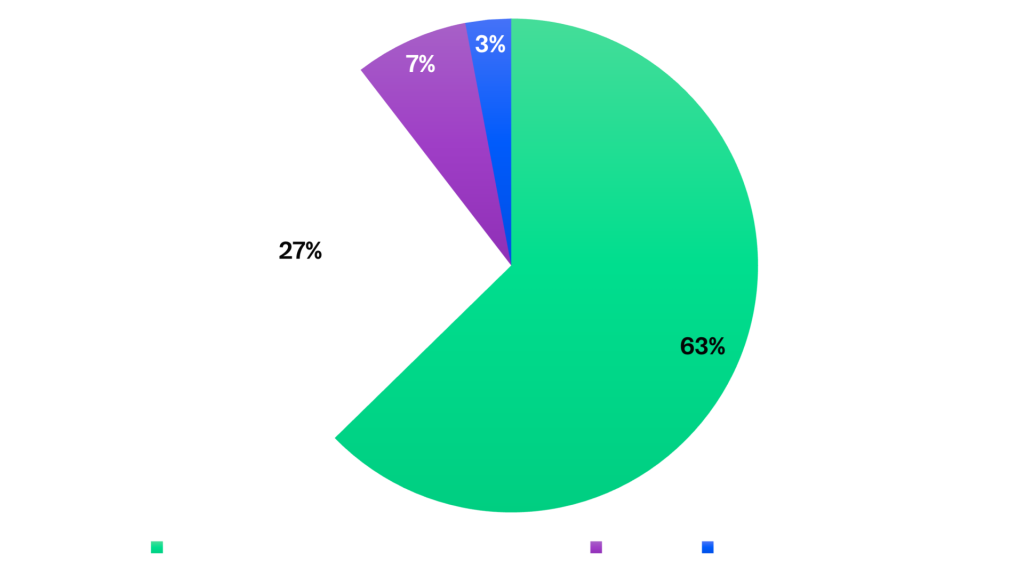
Where EMA is Focusing its GCP Inspections
Of the 67 inspections, the majority targeted clinical investigator sites (63%), followed by sponsor sites (27%), with fewer inspections at CROs (8%) and analytical laboratories (3%).
This distribution reinforces that inspection readiness is not just a sponsor-level concern; it is also heavily focused on site-level documentation. As a result, regulators are closely scrutinising the completeness, accuracy, and ongoing maintenance of essential documents held at investigator sites, particularly the Investigator Site File (ISF).
Figure 2: GCP Inspections by Site Type – 2024
Which EMA GCP Categories Had the Most Major or Critical Findings?
Across all inspections, inspectors identified 335 major or critical compliance gaps, of which over 96% were classified as major. A substantial proportion of these findings were in the general and trial management categories.
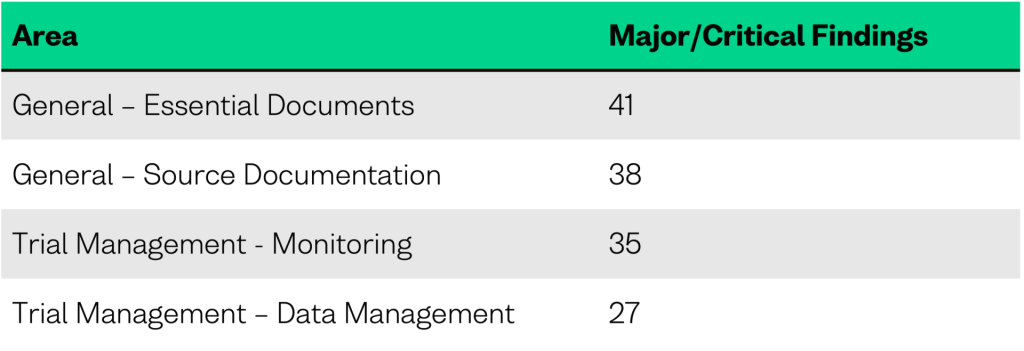
1. Essential Documents: The Most Significant EMA Finding
Compliance gaps related to essential documents represent the single largest category of major and critical findings in the 2024 report. Within this subcategory there is a lack of access at the trial site to trial-relevant electronic systems containing essential documents and data, limiting the ability of monitors and inspectors to perform effective oversight.
Also included within Essential Documents, are issues with Trial Master Files (TMFs) and Investigator Site Files (ISFs), including files that were incomplete, poorly maintained, or not inspection-ready. In some cases, organisations may lack effective version control and document management practices, resulting in missing version histories, inconsistencies between protocols and investigator brochures, and the absence of formally documented TMF quality control processes.
Additionally, this subcategory covers possible weaknesses in processes for the certification and quality of document copies. Certification procedures may be poorly defined or absent, and in some instances source data verification may rely on uncertified copies of electronic medical records, raising potential concerns regarding data reliability and traceability. Taken together, these types of findings highlight areas where inspection readiness and governance of essential trial documentation may require strengthening.
2. Source Documentation: Ongoing Data Integrity Concerns
Source documentation continues to be a significant area of regulatory concern. In this subcategory inspectors may report incomplete, inaccurate, or non-contemporaneous source data, undermining confidence in the reliability of trial results. Discrepancies between source data and case report forms (CRFs), indicating weaknesses in data transcription, review, and verification processes.
In addition, inspectors may note inadequate documentation of key trial processes, including gaps in the recording of clinical procedures and sample handling. These failings limit traceability and make it difficult to reconstruct trial conduct during inspections, particularly when source records are dispersed across multiple systems or locations.
3. Monitoring: Overlapping Weaknesses in Data Oversight
Monitoring-related findings remain a big area of focus and frequently overlap with broader issues related to source documentation and essential records. This subcategory describes potential weaknesses in the detection and escalation of issues during routine monitoring activities. These may include delays in serious adverse event (SAE) reporting, missing Investigator Site File (ISF) documentation, unreported protocol deviations, or missing laboratory values that were not identified through monitoring processes.
A notable theme within this category relates to limitations in monitor access to source data. In some inspections, Clinical Research Associates (CRAs) may not have direct access to electronic health records (EHRs) or electronic medical records (EMRs), which can limit their ability to conduct comprehensive monitoring. As a result, not all available source data may be reviewed, reducing the effectiveness of monitoring as a key control for trial quality oversight and participant safety.
4. Data Management: System Validation & Governance Gaps
Data management deficiencies continue to pose risks to data integrity and regulatory confidence. One example could be a lack of formal data management plans, procedures, and oversight, particularly in complex or multi-vendor trial environments.
Weaknesses in data migration and system validation may also be observed, raising concerns about the accuracy and completeness of transferred data. Within this subcategory there may be instances where sensitive trial data is managed using formats such as Excel, this would be deemed non-compliant as it fails to provide adequate controls, audit trails, and documented traceability of data handling activities.
This subcategory may also include inadequate version control and insufficient datetime stamping of datasets and analysis outputs, which can limit the ability to demonstrate data provenance and reproducibility. Additionally, the absence of formal processes for identifying, documenting, and reporting protocol deviations can increase potential risks to data integrity.
Conclusion: EMA’s 2024 GCP Findings Highlight an Urgent Need for Stronger Data Governance
The EMA’s 2024 GCP findings highlight the need for stronger control over clinical trial data and documentation across their full lifecycle. Many of the observed compliance gaps stem from data sprawl, limited access to records, and weak long-term governance.
To address essential document findings, organisations should implement centralised, validated systems for managing TMFs and ISFs, with clear version control, audit trails, and defined quality control processes. Ensuring inspection-ready access to trial documentation including certified copies is critical for both sites and sponsors.
Improvements in source documentation and monitoring require better data traceability and access. Providing monitors and inspectors with controlled access to electronic source records, supported by complete audit trails and appropriate system controls, enables effective oversight and strengthens data integrity and GCP compliance.
Data management findings further emphasise the need for formal data governance, validated systems, and secure long-term retention of clinical data and analysis outputs. Reliance on short-term or non-validated tools increases regulatory risk, particularly as systems are retired or data is migrated.
The original PDF of the EMA annual report of Good Clinical Practice can be accessed here: Annual Report of the Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Inspectors’ Working Group (IWG) 2024
Further information
Supporting 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance with Arkivum
Applying the ALCOA+ principles to archived GxP data | Arkivum

Anthony Wells
Anthony assumed the role of Product Marketing Manager at Arkivum in 2024, leveraging over a decade of experience of product marketing management in the technology sector. Proficient in developing and executing marketing strategies, Anthony is also experienced in product lifecycle management, from inception through to discontinuation.
Get in touch
Interested in finding out more? Click the link below to arrange a time with one of our experienced team members.
Book a demo